The matrix below details the areas of advanced AI capabilities in which consumer and foodservice companies should focus their time and resources. The matrix is also relevant to packaging companies' operations in R&D and innovation, manufacturing, and distribution and logistics. We suggest that companies invest in technologies shaded in green, explore the prospect of investing in technologies shaded in yellow, and ignore areas shaded in red.
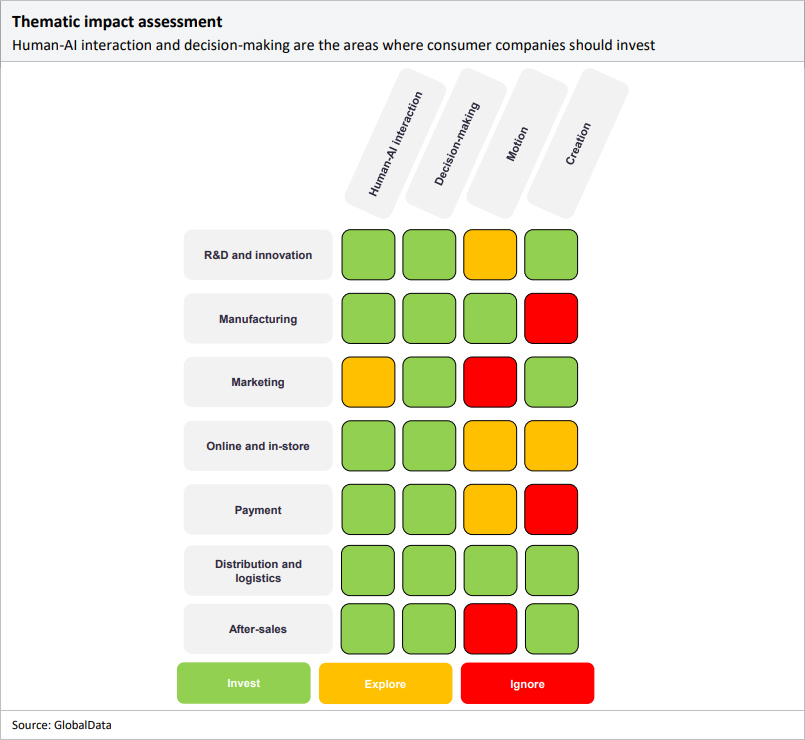
Every area of the consumer value chain could benefit from more than one AI technology. Human-AI interaction capabilities include computer vision (CV) and conversational platforms. CV technology is used to interpret images and videos and can be used for quality assurance in manufacturing and distribution processes. PepsiCo-brand Frito-Lay uses CV in its chip manufacturing to predict the weight of potatoes.
This saved the company $300,000 per factory line in the US. CV can also be used in the foodservice industry to check product quality, like Domino's DOM Pizza Checker, which checks for pizza type, correct toppings, and aesthetic appeal. CV for quality assurance should also be implemented across consumer factories and packaging plants to automate packaging processes. Conversational platforms have multiple use cases, including improving online experiences, customer service, and after-sales support.
Decision-making capabilities include any AI technology, such as machine-learning (ML) and data science, that help companies plan, identify, classify, and forecast. Predictive and behavioural analytics models can be used to curate new product offerings based on emerging customer needs and target marketing campaigns to desired audiences. Predictive analytics can also provide end-to-end supply chain visibility for consumer, foodservice, and packaging companies.
AI algorithms are also used to detect fraud in payment procedures and determine customer suitability in buy now, pay later (BNPL) schemes. Predictive maintenance models are used in manufacturing and distribution to reduce machine downtime and optimise distribution schedules. Mondi uses predictive maintenance tools across its paper manufacturing plants to save over $54,000 annually on repairs.
Decision-making AI capabilities can automate and streamline recruitment and onboarding, helping large consumer goods companies significantly reduce time spent on repetitive tasks. The motion category includes smart robots and motion control sensors common across manufacturing and distribution channels.
Restaurant chains like Domino's and Jollibee's have tested smart waiter robots and autonomous delivery vehicles. These have not been widely adopted and are used as a novelty rather than a cost-cutting measure. Generative AI incorporates AI algorithms that can generate audio, text, or images similar to the data on which it was trained. It is a relatively new AI technology, and adoption in the consumer goods industry has so far been limited.
Generative AI will help simplify data analytics and improve marketing and customer service experiences. Nestlé, General Mills, and AB InBev have already adopted GPT-4 to aid with interpreting data in business intelligence. Coca-Cola is using ChatGPT and DALL-E 2 to create marketing campaigns.
How AI helps resolve the challenge of high inflation
Consumer goods, foodservice, and packaging companies are experiencing rising production, manufacturing, and distribution costs. AI can help to keep costs down by optimising processes and reducing waste. AI technologies can act as smart managers, analysing thousands of data points at any given time, allowing companies to optimise operations and reduce costs on various fronts.
Some examples include automating stock inventory operations based on predicted demand to reduce waste, performing quality assurance with CV to reduce mistakes, and optimising staffing. In the foodservice industry, AI solutions developed by 7Shifts and Medallia forecast staffing needs based on a range of inputs, from historical sales to the weather, and automate scheduling, optimising labour costs.
Dragontail Systems, a subsidiary of Yum! Brands, has developed an AI-powered algorithm that can schedule drivers, predict preparation and delivery times, and suggest real-time operational improvements.
While the initial investment required can be high, AI technologies have significant return-on-investment (ROI) rates. Investing in AI technologies will not protect companies against the full impact of high inflation. However, it can reduce operational costs when sales volumes are down, boosting internal growth rates. Automating supply chains with AI can also improve supply chain resilience, future-proofing a company's supply chain against disruptive events that may cause inflation to rise again.
How AI helps tackle the challenge of ESG
AI can be used in product development to create more sustainable the ethically sourced products. In 2021, Unileverbeauty brand Hourglass relaunched its Red 0 lipstick. Previously, the lipstick had been formulated with carmine - a pigment that requires over 1,000 crushed beetles per product. Using AI, the brand could analyse colour combinations to formulate a cruelty-free identically coloured alternative.
AI can also help reduce waste, a prominent issue across the consumer goods, foodservice, and packaging industries. In 2022, Nestlé created the Institute of Agricultural Sciences to study how AI can help farmers improve their environmental footprint. Similarly, AB InBev has used its AI-powered Smart Barley platform for a decade.
The platform helps farmers improve their yields and reduce water and fertilizer use. In the foodservice industry, Winnow develops AI-enabled tools that take photos and weigh discarded food, helping commercial kitchens measure, monitor, and reduce food waste.
AI-powered predictive maintenance can help reduce energy consumption in manufacturing and distribution centres. Predictive maintenance uses sensors to continuously monitor the condition of machines and other equipment in factory lines and predict when maintenance is required. This approach can reduce energy consumption and the costs of maintenance.
For example, Colgate-Palmolive uses Augury's AI sensors to monitor water cooling systems in its factories. In one instance, it saved 192 hours of machine downtime after preventing a failure from overheating.
AI-powered robotic systems can also automate the recycling process. Companies such as AMP Robotics and EverestLabs use CV to recognise patterns in recyclable materials, such as size and colour. An AI algorithm then communicates with robotic arms that sort material based on those characteristics.
Adoption of these technologies across the consumer goods and packaging industries will make recycling more affordable, less time-consuming, and make the industries more sustainable.
Heavy goods transportation is responsible for 9% of global emissions. Autonomous vehicles (AVs) will revolutionise the distribution of consumer goods, making transportation more efficient and eliminating worker restrictions such as driver rests and night shifts. Taking the driver out of the equation will also reduce costs associated with human error and maintenance. However, AV adoption is still in its early stages.
How AI helps resolve the challenge of supply chain management
Supply chain disruption caused by the Covid-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions pressured companies to accelerate the digitalisation of supply chains. Automating supply chains can help reduce costs, minimise supply peaks and troughs, and ensure supply availability all year round.
Predictive analytics can be used to predict the supply needed based on consumer interest and sales figures. Procter & Gamble (P&G) used its in-house AI predictive analytics platform to manage supply chain disruption caused by the pandemic at a time when consumer spending was unpredictable. P&G claims that this and other AI applications, including monitoring stock inventory during the phasing in and out of products, have saved the company $60 million annually.
By creating a digital model of the entire value chain, predictive analytics can offer complete visibility of supply chain operations from start to finish. In collaboration with o9 Solutions, Estee Lauder launched an AI-backed supply and demand planning tool that improved its forecasting accuracy by 30%. AI can also help monitor the quality of ingredients throughout the supply chain. In collaboration with ThinkIQ, General Mills has used sensors and machine vision to track the movement of ingredients and ensure that gluten-free products remain gluten-free.
How AI helps tackle innovation and changing consumer preferences
Brands need to understand consumer behaviour and cater to changing consumer needs and preferences to be successful. AI-driven data analytics can generate perceptive consumer insights, trend predictions, and forecasting, helping drive innovation by reducing the time to market. This allows companies to be flexible and adaptable to new trends, staying relevant as consumer tastes change.
For example, Nestlé's 14 R&D AI accelerators have reduced new product development time from 33 to 12 months. Generative AI can also help with product creation. In March 2023, AB InBev announced Beck's Autonomous, the world's first fully AI-generated beer. The company used ChatGPT and MidJourney to curate a recipe, design the packaging, and create a marketing campaign.
In R&D, large consumer goods companies use data lakes to test new formulations. Unilever uses AI-powered data analysis to formulate beauty and skincare products for Vaseline, Dove, and Pond's.
Unilever data scientists use AI to test over 100 trillion microbes and their effects on the human immune system. Using 12 terabytes of data, the company can formulate new skincare products to help resolve issues raised by the data. This type of extensive data analysis is impossible to conduct without AI.
Companies can also use customer data and social media analytics to curate new product offerings based on customer preferences. In 2019, Coca-Cola released Sprite Lymonade, Sprite Cherry, and Orange Vanilla Coke after analysing customers' social media accounts. Similarly, Ben & Jerry's used AI to analyse trending songs, videos, and social media to curate a new ice cream flavour - Fruit Loops and Frozen Flakes.
AI can also help target the right audiences. It can use customer data to personalise shopping experiences and create targeted ads in real-time. Starbucks and Dunkin Donuts use AI-powered data analytics in their apps to personalise recommendations based on customers' previous purchases.
Convenience is becoming an increasingly important factor among younger generations. AI can enhance the customer experience in the foodservice industry by allowing faster and more streamlined services. Fast-food giants, including McDonald's, Wendy's, and Panera, have automated drive-thru experiences using a combination of conversational platforms. In February 2023, McDonald's first fully automated drive-thru received mixed reviews, with the AI occasionally misunderstanding customer orders.
However, as AI accuracy increases, these issues should subside. In convenience stores and event spaces, frictionless checkouts are becoming increasingly common. In 2022, Leicester FC became the first English stadium to open a frictionless 'Tap+Go' bar. Using AiFi's CV technology, customers can purchase food and beverages from the store without waiting in line or stopping to scan or pay.
How AI helps resolve the challenge of the future of work
The future of work is increasingly digital, with AI automating repetitive tasks across the consumer goods value chain. On the business intelligence side, AI is automating repetitive tasks across management, legal, and HR departments. Unilever, Nestlé, and PepsiCo have all adopted ML algorithms in recruitment and onboarding processes. ML algorithms can assess the suitability of candidates, while conversational platforms can help answer questions asked by new employees.
Companies have also started exploring how to increase productivity with the help of generative AI. Significant human input is still necessary when using large language models (LLMs) as they do not have in-built fact-checking capabilities, and their output can be rudimentary and lack understanding.
However, as generative AI gains greater accuracy, it will be adopted in press release writing, contract drafting, sales proposal writing, budget drafting, and customer service. Creating LLMs can be an expensive investment. Consumer goods companies should instead purchase pre-trained LLMs, such as GPT-4, and train the models with company data.
AI can also create safer work environments. According to the UK Department of Transportation, over 90% of car accidents are caused by human error, with 30% of accidents involving people driving for work. AI-powered autonomous vehicles (AVs) will improve long-haul and delivery driver safety and increase journey efficiency.
There is some concern that drivers will lose their jobs to this technology. However, autonomous trucks currently available for enterprise use still require significant human input. Drivers' responsibilities will become more akin to piloting commercial aircraft rather than physically driving the vehicle. Fully autonomous vehicles are still some time away, with widespread adoption even further off.
In factory lines, AI can also quickly analyse a vast amount of data and identify any anomalies or patterns. It allows for the early detection of potential hazards and the prevention of dangerous incidents. Similarly to predicting accidents, AI can also anticipate equipment malfunctions. AI systems can notice patterns of a machine malfunctioning over time and alert when a machine needs to be replaced.
GlobalData, the leading provider of industry intelligence, provided the underlying data, research, and analysis used to produce this article.
GlobalData’s Thematic Intelligence uses proprietary data, research, and analysis to provide a forward-looking perspective on the key themes that will shape the future of the world’s largest industries and the organisations within them.